[ad_1]
If China turns into a constant internet exporter of maize, South Africa must discover markets elsewhere
One thing vital for international agriculture occurred this previous week however obtained minimal media protection. The Chinese language Nationwide Crop Selection Approval Committee launched two requirements that clear the trail for cultivating genetically modified (GM) crops within the nation.
This has been the lacking piece within the rules for the business rising of genetically modified maize and soybeans in China. The federal government has two steps in these rules. These are a “security certificates” and a “selection approval” earlier than crops might be commercially cultivated.
Varied genetically modified maize and soybean varieties have obtained the protection certificates since 2019. What’s been lacking has been the “selection approval”. Now that hurdle has been cleared and commercialisation of genetically modified crops in China is an actual risk.
This message was additionally echoed by the Chinese language Agriculture Ministry. It famous that “China plans to approve extra genetically modified (GM) maize varieties.” At present, China imports genetically modified maize and soybean however prohibits home cultivation of the crops.
The change in rules would doubtlessly result in an enchancment in yields. That is aligned with China’s ambition of changing into self-sufficient in important grains and oilseeds within the coming years. There are particular targets in merchandise like pork, the place the nation desires to provide 95% of its consumption by 2025.
South African farmers and agribusinesses must pay shut consideration to those developments as a result of it’s going to have an effect on the long-term progress of the home agricultural sector.
The rise in manufacturing in different elements of the world, particularly in maize, the place South Africa is a internet exporter, might carry elevated competitors and downward strain on costs within the medium time period. A few of South Africa’s key maize export markets are South Korea, Japan, Taiwan and Vietnam. All have proximity to China.
If China progressively will increase manufacturing and turns into a constant internet exporter of maize, South Africa must discover markets elsewhere. This may be a problem.
The talk
China’s maize yields are comparable with South Africa, the USA, Argentina and Brazil, which have lengthy adopted the genetically modified seeds (see Exhibit 1).
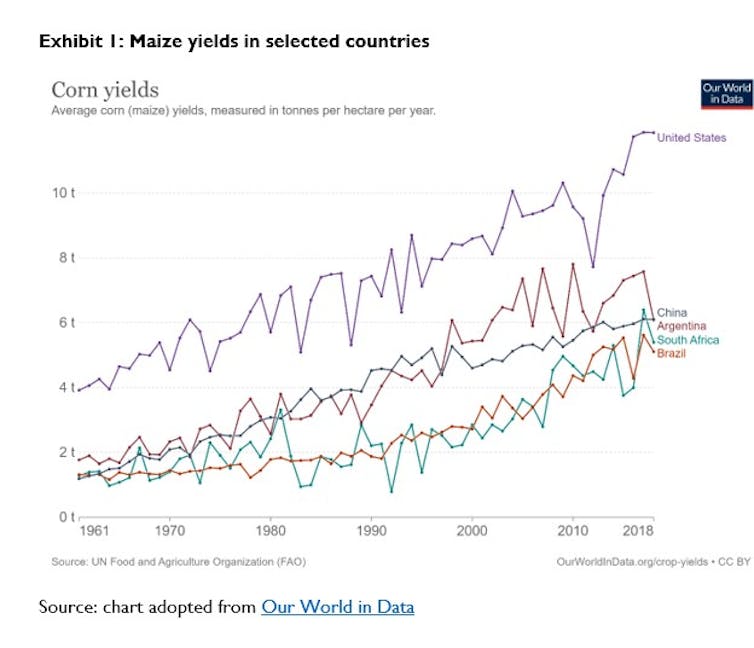
In these international locations, amongst others, genetically modified seeds have had further advantages comparable to reducing insecticide use, inspired extra environmentally pleasant tillage practices and crop yield enhancements.
If maize and soybean yields enhance within the coming years, China’s import dependence might reduce.
China is likely one of the world’s largest maize and soybean importers. The nation accounted for 13% of world maize imports in 2021 and roughly 60% of the world’s soybean imports. Decreasing import volumes is prone to result in downward strain on international costs.
A discount within the international maize and soybeans costs could be optimistic for shoppers and the livestock and poultry sectors. That is a lot wanted because the world has been in a interval of elevated meals costs over the previous two years.
That is unlikely to occur throughout the subsequent two seasons as widespread planting of GM crops in China will possible take a while. China has been sluggish in GM adoption, however made important progress in gene modifying, which has totally different rules, and has helped enhance the crop yields.
The results
There are classes right here for the African international locations, most of which have resisted the cultivation of genetically modified crops. South Africa is the exception.
In keeping with the Worldwide Grains Council, South Africa produces about 16% of sub-Saharan maize, utilizing a comparatively small space of a median of two.5 million hectares since 2010. In distinction, international locations comparable to Nigeria planted 6.5 million hectares in the identical manufacturing season however solely harvested 11.0 million tonnes of maize, equating to fifteen% of the sub-Saharan area’s maize output.
Irrigation has been an added consider South Africa, however to not a big extent, as solely 10% of the nation’s maize is irrigated, with 90% being rainfed. That is much like different African international locations.
South Africa started planting genetically engineered maize seeds within the 2001/02 season. Earlier than its introduction, common maize yields have been round 2.4 tonnes per hectare. This has now elevated to a median of 5.6 tonnes per hectare as of the 2020/21 manufacturing season.
In the meantime, the sub-Saharan African maize yields stay low, averaging under 2.0 tonnes per hectare. Whereas yields are additionally influenced by improved germplasm (enabled by non-genetically modified biotechnology) and improved low and no-till manufacturing strategies (facilitated by way of herbicide-tolerant GM know-how), different advantages embody labour financial savings and lowered insecticide use in addition to enhanced weed and pest management.
With the African continent at the moment struggling to fulfill its annual meals wants, utilizing know-how, genetically modified seeds, and different means must be an avenue to discover to spice up manufacturing. The advantages of a rise in agricultural output are evident in Argentina, Brazil, the USA, and South Africa.
Many African governments ought to reevaluate their regulatory requirements and embrace know-how. In fact, this usually introduces debates in regards to the possession of seeds and the way smallholder farmers might wrestle to acquire seeds in some growing international locations.
These are realities that policymakers within the African international locations ought to handle when it comes to reaching agreements with seed breeders and know-how builders however not shut off innovation. The know-how builders additionally have to be conscious of those issues when partaking varied governments within the African international locations.
Geopolitical and local weather change dangers current the urgency to discover the technological options to extend every nation’s agricultural manufacturing. The Chinese language regulators are following that path.![]()
Wandile Sihlobo, Senior Fellow, Division of Agricultural Economics, Stellenbosch College
This text is republished from The Dialog underneath a Artistic Commons license. Learn the unique article.
We’re a voice to you; you will have been a help to us. Collectively we construct journalism that’s impartial, credible and fearless. You may additional assist us by making a donation. This may imply so much for our potential to carry you information, views and evaluation from the bottom in order that we are able to make change collectively.
[ad_2]
Source link

