[ad_1]


One97 Communications owned ‘Paytm’ is India’s main digital ecosystem for customers and retailers. The corporate provides cost companies, commerce and cloud companies, and monetary companies to greater than 33 crore registered customers and a couple of crore registered retailers, as of June 30, 2021 . Customers use the corporate’s platform for cost companies equivalent to cash switch, in-store funds, invoice funds and monetary merchandise equivalent to private loans, bank cards, insurance coverage and funding options. The corporate holds a 49 per cent stake in its affiliate Paytm Funds Financial institution by means of which it supplies companies equivalent to wallets, FASTags, financial institution accounts and UPI companies. Paytm Funds Financial institution is the one worthwhile arm of Paytm.
However, retailers to this platform get entry to cost choices equivalent to QR code and cost gateways. Lenders and insurance coverage suppliers additionally use the corporate’s platform to extend their shopper base.
The corporate generates revenues from cost and monetary companies primarily within the type of transaction charges charged from its retailers, shopper comfort charges charged for sure varieties of transactions equivalent to flight, practice and bus bookings, and subscription charges for sure merchandise, equivalent to Paytm Soundbox and POS. For monetary companies, the corporate costs sourcing charges from monetary establishment companions and assortment charges. This section accounted for 75.3 per cent of its revenues in FY21, whereas the remainder comes from commerce (in-store gross sales) and cloud companies.
Strengths:
- Its model ‘Paytm’ is without doubt one of the most famed cost manufacturers in India.
- Paytm can be the biggest cost platform in India when it comes to numbers of transactions with GMV (Gross service provider worth) of Rs 4,033 billion in FY21. It processed a complete of 5.9 billion service provider transactions. Within the second quarter of the present fiscal yr, its GMV stood at Rs 1,956 billion as in comparison with Rs 947 billion in the identical interval final yr.
- As per RedSeer, Paytm has a funds transaction quantity market share of 40 per cent and pockets funds transaction market share of 65-70 per cent in India in FY21.
- The corporate’s investor record consists of among the most outstanding names equivalent to Softbank, Warren Buffett, and Ant Group.
Weaknesses:
- The corporate has a historical past of incurring losses. Nonetheless, its losses have narrowed down from Rs 4,225 crore in FY19 to Rs 1,701 primarily on account of discount in advertising and promotional bills.
- Though the corporate has been rising when it comes to GMV which has elevated from Rs 2,292 billion in FY19 to Rs 4,033 billion in FY21, it has to retain its consistency of progress with a view to flip worthwhile.
- The corporate has additionally been burning money and has incurred greater than Rs 8,900 crore of money outflow from working actions.
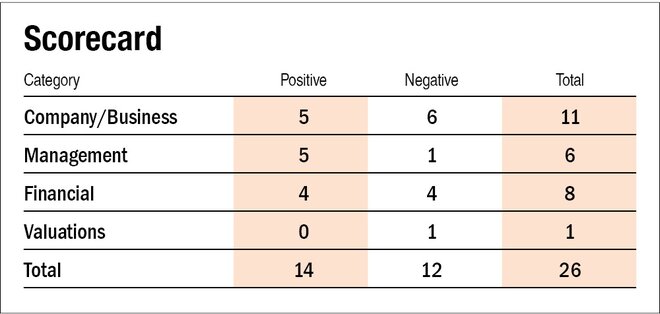
IPO questions
The corporate/enterprise
1) Are the corporate’s earnings earlier than tax greater than Rs 50 crore within the final 12 months?
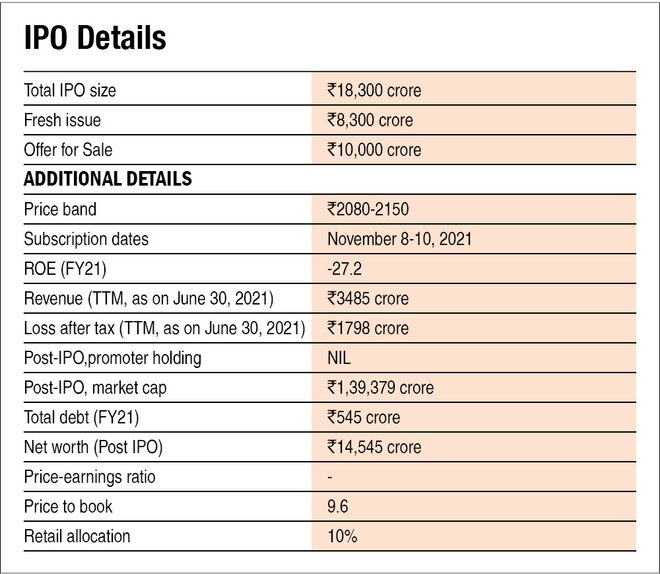
No, the corporate reported a loss earlier than tax of Rs 1,788 crore within the final 12 months ending June 30, 2021.
2) Will the corporate be capable to scale up its enterprise?
Sure, the corporate has an asset-light enterprise mannequin, which permits it to scale up its enterprise sooner than conventional companies. Together with this, growing variety of smartphone customers and rising web penetration will additional propel demand for digital cost as it’s a easy, protected and handy means of transferring cash.
3) Does the corporate have recognisable model/s, actually valued by its prospects?
Sure, the corporate’s model ‘Paytm’ is without doubt one of the most famed manufacturers in India and is the biggest cost platform in India when it comes to variety of transactions.
4) Does the corporate have excessive repeat buyer utilization?
Sure, the corporate claims that GMV generated by customers acquired in FY17 have elevated by 6.8 instances by FY21 which clearly signifies the repeat buyer utilization.
5) Does the corporate have a reputable moat?
No. Though the corporate is a market chief within the cost companies, it doesn’t have a definite credible moat to safeguard its enterprise.
6) Is the corporate sufficiently strong to main regulatory or geopolitical dangers?
No, as the corporate is engaged in cost gateway companies, banking and pockets enterprise and broking and insurance coverage associated enterprise, it has to stick to varied rules from RBI, SEBI, and IRDAI.
7) Is the enterprise of the corporate resistant to simple replication by new gamers?
No. Since it’s a technology-based firm, its enterprise mannequin may be simply replicated. Nonetheless, constructing a model picture like Paytm may be troublesome.
8) Is the corporate’s product in a position to stand up to being simply substituted or outdated?
Sure. Growing tempo of digitalisation and wider acceptance of digital cost together with authorities initiatives in the direction of a cashless financial system, will safeguard the corporate’s merchandise equivalent to cost companies from being outdated.
9) Are the purchasers of the corporate devoid of great bargaining energy?
The corporate has two classes of consumers. One: people who obtain the app and make funds. Two: retailers who obtain funds.
Particular person payers successfully have very excessive bargaining energy as a result of they at present pay nothing and if Paytm ever tries to cost for funds, they are going to instantly transfer to different apps. Retailers too sometimes settle for funds by means of all digital means and actively information their prospects to make use of cost apps that they discover extra enticing.
Successfully, Paytm’s prospects have very excessive bargaining energy as a result of they’re able to implement zero or close-to-zero pricing on the corporate.
10) Are the suppliers of the corporate devoid of great bargaining energy?
No, the corporate’s suppliers embrace know-how suppliers which are not devoid of any important bargaining energy. Additionally, the top-10 suppliers accounted for greater than 61 per cent of complete bills in FY21 which reveals consolidation of the bills to some suppliers.
11) Is the extent of competitors the corporate faces comparatively low?
No, the corporate faces competitors from different cost suppliers equivalent to Google Pay and PhonePe.
Administration
12) Do any of the corporate’s founders nonetheless maintain no less than a 5 per cent stake within the firm? Or do promoters completely maintain greater than a 25 per cent stake within the firm?
Sure, the founding father of the corporate Vijay Shekhar Sharma will maintain 8.9 per cent stake within the firm post-IPO.
13) Do the highest three managers have greater than 15 years of mixed management on the firm?
Sure, its CEO and founder Vijay Shekhar Sharma has been related to the corporate since its inception in 2000.
14) Is the administration reliable? Is it clear in its disclosures, that are in keeping with SEBI tips?
Sure, we’ve no cause to consider in any other case.
15) Is the corporate freed from litigation in court docket or with the regulator that casts doubts on the intention of the administration?
No, there are tax proceedings to a tune of Rs 3,733 crore in opposition to the corporate.
16) Is the corporate’s accounting coverage secure?
Sure, we’ve no cause to consider in any other case.
17) Is the corporate freed from promoter pledging of its shares?
Sure, because the firm is professionally managed, it doesn’t have any identifiable promoter.
Financials
18) Did the corporate generate a present and three-year common return on fairness of greater than 15 per cent and a return on capital of greater than 18 per cent?
No, the corporate has incurred losses within the final three fiscal years.
19) Was the corporate’s working money movement constructive through the three years?
No, the corporate has reported destructive working money movement over the past three years.
20) Did the corporate improve its income by 10 per cent CAGR within the final three years?
No, the corporate’s income decreased by 6.9 per cent CAGR within the final three years.
21) Is the corporate’s web debt-to-equity ratio lower than one or is its interest-coverage ratio greater than two?
Sure, the corporate has a debt-to-equity ratio of 0.07 as of June 2021 with no long-term debt.
22) Is the corporate free from reliance on large working capital for day-to-day affairs?
Sure. The corporate has a robust money place with constructive working capital and has a destructive working capital cycle of 67 days which implies that it collects money earlier than it has to pay its collectors.
23) Can the corporate run its enterprise with out counting on exterior funding within the subsequent three years?
No, the corporate has been burning money and has reported an working money outflow of Rs 8,900 crore within the final three years. Though the corporate is elevating Rs 8,300 crore from the IPO, it’d want exterior financing sooner or later.
24) Have the corporate’s short-term borrowings remained secure or declined (not elevated by larger than 15 per cent)?
Sure. The corporate’s short-term borrowings decreased by 31.6 per cent from FY19 – Rs 696 crore to Rs 476 crore, as of June 30, 2021.
25) Is the corporate free from significant contingent liabilities?
Sure, the corporate has contingent liabilities of Rs 5.2 crore, which is just 0.84 per cent of its fairness, as of June 30, 2021.
Inventory/valuations
26) Does the inventory provide an operating-earnings yield of greater than 8 per cent on its enterprise worth?
No, the corporate has been reporting destructive working earnings over the past three years.
27) Is the inventory’s price-to-earnings lower than its friends’ median stage?
Not relevant. No different listed corporations are concerned in an identical line of enterprise. The corporate has reported destructive earnings over the past three years.
28) Is the inventory’s price-to-book worth lower than its friends’ median stage?
Not relevant. Put up-IPO, the corporate’s inventory will commerce at a P/B of 9.6 instances.
Disclaimer: The authors could also be an applicant on this Preliminary Public Providing.
[ad_2]
Source link

