[ad_1]
The Reserve Financial institution of India (RBI) raised the benchmark coverage repo charge, or the speed at which it lends short-term funds to banks, by 50 foundation factors to 4.9% in its June coverage assertion as client inflation has been persistently above the higher band of 2-6percenttarget.
One foundation level is 0.01%.
“If this inflation is allowed to exit of hand, it might corrode the foundations of the restoration that’s regularly gaining traction — empirical proof exhibits that inflation above 6% in India is unambiguously dangerous for development,” MPC’s inside member and RBI deputy governor Michael Patra was cited as saying within the minutes.
The RBI transfer was aimed toward guaranteeing value stability even whereas recognising that development initiatives nonetheless deserved a serving to hand from the Mint Highway.
Monitoring World Developments
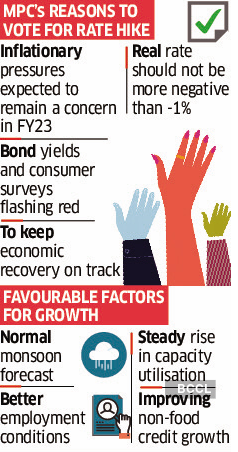
Elements giving MPC members consolation on the expansion outlook embody forecast of a standard southwest monsoon, the development in employment circumstances, regular rise in capability utilisation and enhancing non-food credit score development.
“This motion will reinforce our dedication to cost stability — our main mandate and a prerequisite for sustainable development over the medium time period,” stated RBI governor Shaktikanta Das.
Altering the course of inflation trajectory to achieve the focused degree is a precedence for the MPC regardless of modest development prospects, stated exterior member Shashank Bhide, who’s a senior advisor on the NCAER.
Between April and June, the MPC raised the coverage charge by 90 foundation factors, however throughout the identical interval the RBI’s projection of inflation for FY23 has risen 100 foundation factors — from 5.7% to six.7%. The true coverage charge, subsequently, stays kind of the place it was in April, implying that additional charge will increase are wanted to get the actual coverage charge within the optimistic zone.
“This jogs my memory of Lewis Carroll’s adage that we should run as quick as we are able to, simply to remain in place, and to go wherever we should run even quicker,” stated exterior member Jayant Varma, a professor at IIM Ahmedabad. “Clearly, extra must be carried out in future conferences to deliver the actual coverage charge to a modestly optimistic degree according to the rising inflation and development dynamics.”
The one-year forward actual charge should not be extra unfavorable than -1%, stated exterior member Ashima Goyal, a professor on the Indira Gandhi Institute of Growth Analysis. “A 50- or 60-basis-point hike would obtain this,” Goyal stated, though “additional supply-side motion and readability on international developments are awaited.”
Varma made the case for beginning to transfer towards offering projections of the longer term path of the coverage charge. “This may assist stabilise long-term bond markets and likewise anchor inflation expectations.” As for the coverage stance, the withdrawal of lodging could be non-disruptive to the method of restoration and would strengthen the continuing efforts to fight inflation and anchor inflation expectations, Das stated.
[ad_2]
Source link