[ad_1]

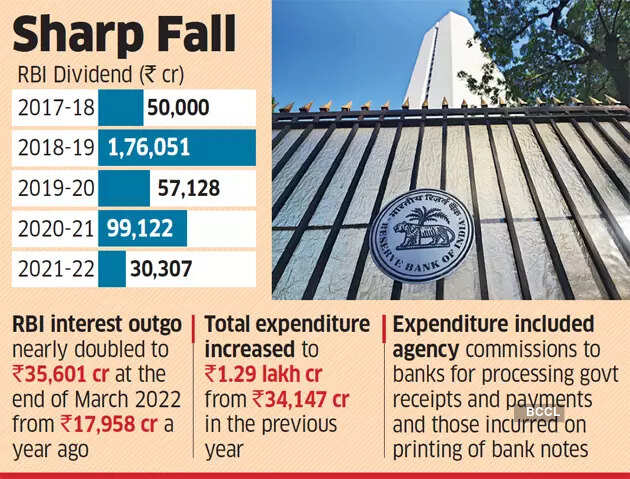
The excess that the Reserve Financial institution of India transferred to the federal government within the final fiscal yr fell sharply primarily because of a soar in expenditure, which was led by curiosity funds to banks on their extra funds parked with it, the financial institution’s annual report confirmed.
Whereas revenue for 2021-22 elevated by 20%, expenditure rose by 280%, which resulted within the general surplus transferred to the federal government lowering 69% to INR 30,307.45 crore from INR 99,122 crore in 2020-21.
Aside from the upper operational expenditure, the RBI additionally needed to pay curiosity on the surplus funds saved by banks with it by the reverse repo window. This curiosity outgo almost doubled to INR 35,601 crore on the finish of March 2022 from INR 17,958 crore a yr in the past.
Whole expenditure in 2021-22 elevated to INR 1.29 lakh crore from INR 34,147 crore within the earlier yr. Expenditure included company commissions to banks for processing authorities receipts and funds, which elevated by 48% to INR 3,859 crore from INR 2,611.05 crore in 2020-21. Expenditure incurred on printing of financial institution notes elevated by 24% to INR 4,985 crore from INR 4,012.09 crore in 2020-21.
Madan Sabnavis, chief economist at Financial institution of Baroda, stated the central financial institution additionally needed to make larger provisions in direction of revaluation of foreign exchange reserves. “A decrease switch to the federal government account signifies that the federal government will fall in need of its INR 74,000 crore assortment goal from RBI, banks and different state-owned monetary establishments,” Sabnavis stated. “Nonetheless, larger tax revenues and proceeds from disinvestments might compensate for this.”
All Expenditure Strains Impacted
Banks might be paying INR 7,867 crore to the federal government as dividend.
“The web curiosity revenue from liquidity adjustment facility (LAF)/marginal standing facility (MSF) operations decreased…because of larger surplus liquidity within the banking system, resulting in larger internet curiosity outgo beneath LAF/MSF and present accounting yr being of twelve months as in comparison with the 9 months interval for 2020-21,” the RBI stated.
All expenditure traces have been impacted as a result of final yr the RBI transitioned to a March closing fiscal yr, making it a nine-month yr. In 2021-22, provisions of INR 1.14 lakh crore and INR 100 crore have been made in direction of switch to the contingency fund (CF) and the asset improvement fund (ADF), respectively.
The CF is a selected provision meant for assembly surprising and unexpected contingencies, together with depreciation within the worth of securities, dangers arising out of financial / trade price coverage operations, and systemic dangers. The stability in CF as on March 31, 2022 was INR 3.10 lakh crore, up from INR 2.84 lakh crore a yr in the past. The cash within the ADF is the supply particularly made until date in direction of investments in subsidiaries and affiliate establishments, and to assist meet inside capital expenditure. Final fiscal, INR 100 crore was supplied on account of recent funding in Reserve Financial institution Innovation Hub (RBIH).
The stability within the ADF as on March 31, 2022 was INR 22,974.68 crore in contrast with INR 22,874.68 crore a yr in the past.
[ad_2]
Source link