[ad_1]
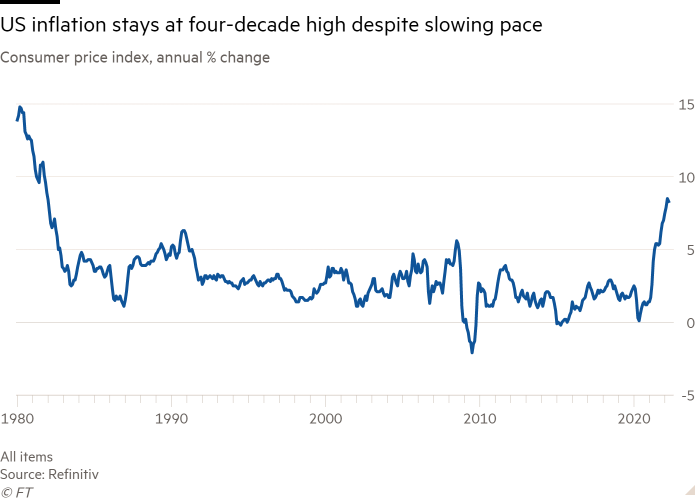
US client costs rose at an annual tempo of 8.3 per cent final month, greater than economists’ expectations and staying at a four-decade excessive, underscoring the urgency of the Federal Reserve’s push to stamp out inflation.
Though the patron worth index moderated for the primary time in eight months — it was a step down from the 8.5 per cent enhance recorded in March — it was barely greater than economists’ expectations of an 8.1 per cent rise. An underlying gauge of inflation additionally rose greater than anticipated, highlighting stresses on households and the problem for the Biden administration.
The information initially jolted the $22tn marketplace for US authorities bonds. The 2-year Treasury yield, which is most delicate to the outlook for financial coverage, jumped roughly 0.12 share factors to 2.73 per cent, earlier than dropping again all the way down to 2.64 per cent. The yield on the benchmark 10-year observe was again under 3 per cent in afternoon buying and selling.
US shares additionally retreated, led by a sell-off in tech, with the Nasdaq Composite down 2.5 per cent and the S&P 500 1 per cent decrease.
“This isn’t the shock both the bond market or the Fed needed,” stated Emily Roland, co-chief funding strategist at John Hancock Funding Administration.
Along with the bounce in costs from final yr, client costs climbed one other 0.3 per cent from the earlier month. That was slower than the 1.2 per cent rise recorded in March, which was fuelled by hovering vitality and meals prices tied to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Shelter, meals, airline fares and new autos had been the biggest contributors to CPI final month. Nevertheless, weak point in vitality costs helped comprise general inflation, with the gasoline index falling 6.1 per cent month on month. That offset will increase in the price of pure gasoline and electrical energy, the Bureau of Labor Statistics, which printed the information, stated.
Stripping out unstable gadgets reminiscent of meals and vitality, nevertheless, the month-to-month rise in core CPI elevated 0.6 per cent final month, in contrast with 0.3 per cent in March. On an annual foundation, that amounted to a 6.2 per cent enhance.
Economists homed in on a 0.7 per cent month-to-month bounce in underlying companies inflation, which excludes vitality companies. Since December, that price has steadily elevated and yr over yr is up practically 5 per cent.
The most recent uptick solidified considerations that worth pressures had been now not a phenomenon unique to sectors most affected by pandemic-related disruptions — however fairly a broad-based pattern affecting all sectors.
“This strikes the stability of dangers to extra concern about inflation going ahead,” stated Eric Stein, chief funding officer for fastened revenue at Eaton Vance.
Nonetheless, the information could characterize the start of a peak within the coronavirus pandemic-era inflation surge attributable to red-hot client demand coupled with extreme provide chain bottlenecks.
Economists broadly anticipate the tempo of client worth development to reasonable farther from these ranges because the speedy results of the warfare in Ukraine abate. The headline annual inflation studying must also begin to fall within the coming months because it begins being in contrast with the very elevated ranges logged final yr.
President Joe Biden on Wednesday stated it was “heartening” to see a moderation within the annual determine, however “the actual fact stays that inflation is unacceptably excessive”. “Inflation is a problem for households throughout the nation and bringing it down is my prime financial precedence,” he stated.
The Fed has elevated its efforts to comprise worth pressures, implementing its first half-point price rise in additional than twenty years this month. Additional such will increase are anticipated in June and July, and doubtlessly even September, with the federal funds price anticipated to succeed in 2.7 per cent by the top of the yr.
The Fed’s discount of its $9tn stability sheet will even begin in June, the second of two levers it’s utilizing to chill the economic system.
The primary query for traders is whether or not the US central financial institution can convey down inflation with out inflicting a recession. John Williams, the president of the New York Fed, stated this week the problem of engineering a mushy touchdown could be tough however “not insurmountable”.
The most recent inflation figures “actually exacerbate a job that was already fairly tough by way of the Fed’s means to engineer a mushy touchdown,” stated Roland at John Hancock. “If inflation stays elevated, it will change into a lot more durable.”
[ad_2]
Source link

