[ad_1]
One fashionable clarification for why the sardine run happens is that the migration could be a relic of spawning behaviour relationship again to the final glacial interval, about 10,000 years in the past

One of many world’s most spectacular marine migrations is the KwaZulu-Natal sardine run. The so-called “biggest shoal on Earth” takes place through the southern hemisphere’s winter.
It includes the motion of tens to a whole bunch of hundreds of thousands of sardines from the warm-temperate waters of South Africa’s south coast to the subtropical waters of the east coast, over a thousand kilometres away.
This annual mass migration, first reported in 1853, is triggered by chilly water upwelling on South Africa’s south-east coast. On this course of, chilly, nutrient-rich water rises up from the deep, making a extremely productive meals net.
The migration attracts huge numbers of predators: the sardine colleges are adopted northwards by seabirds, sharks, seals, dolphins and even giant baleen whales. These devour as lots of the helpless sardines as they will, which is made simpler by the truth that their prey is sandwiched between dry land and the new, tropical waters of the southward-flowing Agulhas Present, which exceed the sardines’ physiological tolerances.
To make issues worse, these fish that survive the predation nonetheless don’t have it simple: The journey is so strenuous that the sardines which finally arrive on the east coast are emaciated. This goes in opposition to what scientists perceive about animal migrations – such large-scale inhabitants actions usually present some “selective benefit” by permitting animals to make optimum use of environmental sources.
Certainly the plain negatives of collaborating within the sardine run should be vastly outweighed by some health advantages to make all of it worthwhile? The reply, our new analysis suggests, is “no” – and the explanations for the sardines’ behaviour lies of their genes.
A definite east coast inhabitants?
One fashionable clarification for why the sardine run happens is that the migration could be a relic of spawning behaviour relationship again to the final glacial interval, about 10,000 years in the past. What’s now subtropical Indian Ocean habitat could have been an vital nursery space with cooler waters.
When the ice age ended, the sardines would have physiologically tailored to tolerate the subtropical circumstances on this area, and advanced into a definite east coast inhabitants that continues to spawn there to at the present time.
These sardines combine with south coast sardines throughout summer time, then separate from them in winter as they migrate up the east coast. The presence of sardine eggs within the plankton confirms that spawning does happen on this area.
Surprisingly, we found that sardines collaborating within the migration usually are not a part of a definite east coast inhabitants. As an alternative, they primarily originate from the colder waters off South Africa’s Atlantic west coast. Why would these sardines migrate to the alternative finish of the nation, solely to finish up in habitat that’s clearly too heat for them? We advise that the fish are drawn into what quantities to an ecological lure – a uncommon instance of a mass migration that has no apparent health advantages.
Genomic analyses
Our analysis began from the idea that the sardine run represents the spawning migration of a definite inventory of sardines that’s physiologically nicely tailored to tolerate subtropical circumstances.
Bodily traits and different knowledge point out that sardines on the east coast are certainly distinct. However this will likely outcome from completely different environmental pressures, together with the stress of collaborating within the migration. We knew that understanding the sardines’ heritable genetic traits would offer stronger proof for this speculation – or debunk it.
So we used 1000’s of genetic markers from throughout the genomes of a whole bunch of sardines captured all through the species’ South African vary. Though most of those markers confirmed little differentiation, a collection of genetic markers with a sign of adaptation to water temperature confirmed regional variations.
We discovered proof for 2 regional populations – but it surely was not the east coast sardines that have been distinct. As an alternative, we discovered genetic variations inside the species’ temperate core vary: one inhabitants was related to South Africa’s cool-temperate west coast (Atlantic Ocean) and the opposite with the warm-temperate south coast (Indian Ocean).
The sturdy affiliation with water temperature means that thermal adaptation maintains these regional patterns; every inhabitants cluster is customized to the temperature vary that it experiences in its native area.
The sardines collaborating within the run confirmed a transparent affiliation with the west coast inhabitants. Not solely are these sardines not nicely tailored to subtropical circumstances, however they really want the colder, upwelled waters of the south-eastern Atlantic Ocean.
Main riddles solved
This research solves a few of the main riddles regarding the sardine run, which make good sense within the mild of the brand new proof.
Our findings clarify why solely a small fraction of the sardines current on the south coast participates within the run. The majority of these sardines are native to this area and are tailored to warm-temperate circumstances. Due to this, they present little curiosity within the chilly, upwelled water.
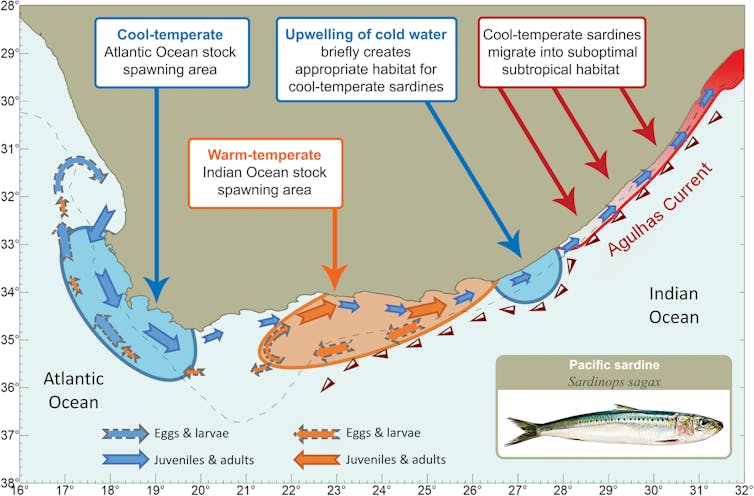
The outcomes additionally present an reason why no sardine runs happen in years when there isn’t a chilly water upwelling. The upwelling on the south-east coast attracts west coast sardines which have dispersed to the south coast, however that aren’t nicely tailored to the hotter water temperatures on this area. They basically take into account the upwelling areas within the south-east to be west coast habitat. For a short while, it’s as if they’re again residence within the Atlantic – however when the upwelling ends and water temperatures rise, their fateful error is revealed.
At this level, the predators have gotten wind of their presence, and because the sardines attempt to escape, they journey ever farther north into unbearably heat subtropical habitat. The destiny of the fish that survive the sardine run is unsure.
Our genomic clarification exhibits that a lot nonetheless stays to be found about how marine life interacts with its surroundings. A substantial amount of integrative, multidisciplinary analysis continues to be wanted earlier than people can effectively and sustainably profit from the unbelievable variety of life and the sources obtainable within the sea.![]()
Peter Teske, Professor of Marine Genomics, College of Johannesburg; Carl van der Lingen, Honorary Analysis Affiliate, College of Cape City; Christopher David McQuaid, Distinguished Professor, Rhodes College, and Luciano Beheregaray, Professor of Biodiversity Genomics, Flinders College
This text is republished from The Dialog below a Inventive Commons license. Learn the unique article.
We’re a voice to you; you’ve got been a help to us. Collectively we construct journalism that’s impartial, credible and fearless. You possibly can additional assist us by making a donation. This may imply rather a lot for our capability to carry you information, views and evaluation from the bottom in order that we will make change collectively.
[ad_2]
Source link

