[ad_1]
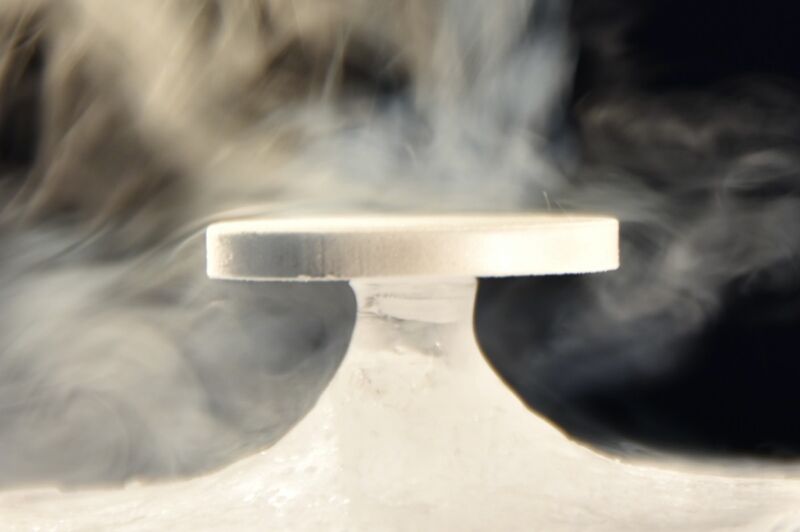

Nicolas Taberlet / Nicolas Plihon
Go to the Small Sea of Lake Baikal in Russia through the winter and you will doubtless see an uncommon phenomenon: a flat rock balanced on a skinny pedestal of ice, akin to stacking Zen stones widespread to Japanese gardens. The phenomenon is typically known as a Baikal Zen formation. The everyday clarification for a way these formations happen is that the rock catches gentle (and warmth) from the Solar and this melts the ice beneath till only a skinny pedestal stays to assist it. The water beneath the rock refreezes at night time, and it has been advised that wind may be an element.
Now, two French physicists imagine they’ve solved the thriller of how these constructions type, in response to a brand new paper printed within the Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences—and their answer has nothing to do with the thermal conduction of the stone. Reasonably, they attribute the formation to a phenomenon referred to as sublimation, whereby snow or ice evaporates straight into vapor with out passing by means of a water part. Particularly, the shade offered by the stone hinders the sublimation charges of the encompassing ice in its neighborhood, whereas the ice additional away sublimates at a sooner price.
Many related formations happen naturally in nature, similar to hoodoos (tall, spindly constructions that type over thousands and thousands of years inside sedimentary rock), mushroom rocks or rock pedestals (the bottom has been eroded by robust dusty winds), and glacier tables (a big stone sitting precariously on prime of a slim pedestal of ice). However the underlying mechanisms by which they type might be very completely different.
As an illustration, as we reported final yr, a workforce of utilized mathematicians from New York College studied the so-called “stone forests” widespread in sure areas of China and Madagascar. These pointed rock formations, just like the famed Stone Forest in China’s Yunnan Province, are the results of solids dissolving into liquids within the presence of gravity, which produces pure convective flows.
On the floor, these stone forests look somewhat much like “penitentes”: snowy pillars of ice that type in very dry air discovered excessive within the Andean glaciers. Charles Darwin described penitentes in 1839 throughout a March 1835 tour during which he squeezed his method by means of snowfields coated in penitentes on the way in which from Santiago, Chile, to the Argentine metropolis of Mendoza. Physicists have been in a position to recreate synthetic variations of penitentes within the lab. However penitentes and stone forests are literally fairly completely different when it comes to the mechanisms concerned of their formation. The spikes of a stone forest are carved by flows, which do not play an enormous function within the formation of penitentes.
Some physicists have advised that penitentes type when daylight evaporates the snow straight into vapor (sublimation). Tiny crests and troughs type, and daylight will get trapped inside them, creating further warmth that carves out even deeper troughs, and people curved surfaces in flip act as a lens, rushing up the sublimation course of much more. An alternate proposal provides an extra mechanism to account for the oddly periodic fastened spacing of penitentes: a mix of vapor diffusion and warmth transport that produces a steep temperature gradient and, therefore, a better sublimation price.
Nicolas Taberlet/Nicolas Plihon
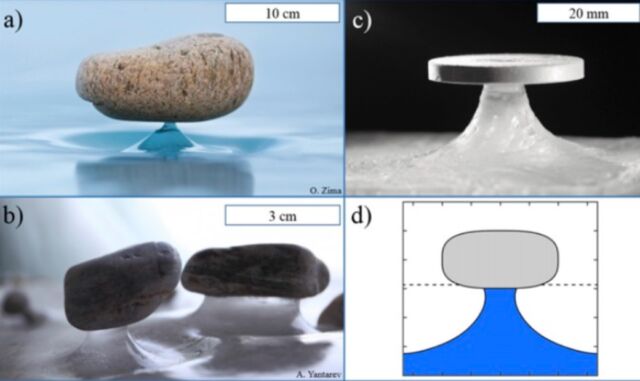
Within the case of the Baikal Zen stone formations, the method appears much like the sublimation speculation for penitentes, in response to co-authors Nicolas Taberlet and Nicolas Plihon of CNRS in Lyon, France. Earlier this month, they printed a considerably associated research in Bodily Evaluate Letters on the pure formation of glacier tables (a rock supported by a slender column of ice). They have been in a position to produce small-scale synthetic glacier tables in a managed setting, and located two competing results that management the onset of glacier desk formation.
With smaller stone caps with increased thermal conductivity, geometrical amplification of the warmth flux causes the cap to sink into the ice. For a bigger cap with much less thermal conductivity, a discount in warmth flux arises from the truth that the cap has a better temperature than the encompassing ice, forming a desk.
For this newest research, Taberlet and Plihon wished to discover the underlying mechanisms behind the pure formation of Baikal Zen constructions. “The shortage of the phenomenon stems from the rarity of thick, flat, snow-free layers of ice, which require long-standing chilly and dry climate circumstances,” the authors wrote. “Climate information present that melting of the ice is just about inconceivable and that, as a substitute, the climate circumstances (wind, temperature, and relative humidity) favor sublimation, which has lengthy been recognized to be attribute of the Lake Baikal space.”
So the researchers set about attempting to breed the phenomenon within the laboratory to check their speculation. They used steel disks as experimental analogs of the stones, putting the disks on the floor of blocks of ice in a industrial lyophilizer. The instrument freezes materials, then reduces the stress and provides warmth, such that the frozen water sublimates. The upper reflectivity of the steel disks in comparison with stones saved the disks from overheating within the lyophilizer’s chambers.
Extraterrestrial
Each aluminum and copper disks produced the Baikal Zen formations, regardless that copper has nearly twice the thermal conductivity of aluminum. The authors concluded that, subsequently, the thermal properties of stone weren’t an important issue within the course of. “Removed from the stone, the sublimation price is ruled by the diffuse daylight, whereas in its neighborhood the shade it creates inhibits the sublimation course of,” the authors wrote. “We present that the stone solely acts as can umbrella whose shade hinders the sublimation, therefore defending the ice beneath, which ends up in the formation of the pedestal.”
This was subsequently confirmed by numerical modeling simulations. Taberlet and Plihon additionally discovered that the dip, or melancholy, surrounding the pedestal is the results of far infrared radiation emitted by the stone (or disk) itself, which boosts the general sublimation price in its neighborhood.
It is fairly completely different from the method that results in glacier tables, regardless of the same form of the 2 formations. Within the case of glacier tables, the umbrella impact is simply a secondary issue within the underlying mechanism. “Glacier tables seem on low-altitude glaciers when the climate circumstances trigger the ice to soften as a substitute of to sublimate,” the authors wrote. “They type in heat air whereas the ice stays at 0 levels Celsius, whereas Zen stones type in air that’s colder than the ice.”
Understanding how these formations happen naturally might assist us study extra about different objects within the universe, since ice sublimation has produced penitentes on Pluto and have influenced panorama formation on Mars, Pluto, Ceres, the moons of Jupiter, the moons of Saturn, and several other comets. “Certainly, NASA’s Europa Lander mission goals to hunt biosignatures on Jupiter’s ice-covered moon, on the floor of which differential sublimation could threaten lander stability, and this must be totally understood,” the authors concluded.
DOI: PNAS, 2021. 10.1073/pnas.2109107118 (About DOIs).
[ad_2]
Source link

